|
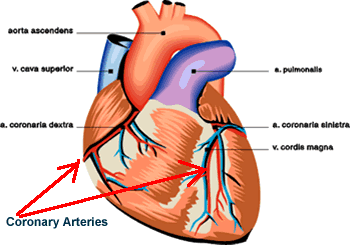
CORONARY ARTERIES The heart is a muscle. Like all muscles and organs of the body, the heart needs oxygen in order to work. Oxygen is carried to the heart muscle by blood vessels. The word "cardiac" means heart. The blood vessels that carry oxygen to the heart muscle are called coronary arteries. They are locate on the outside of the heart muscle (Image 1). Coronary artery disease occurs when fatty deposits collect inside the coronary arteries, narrowing the blood vessel diameter. This makes it difficult for blood to reach the heart muscle. If the narrowing becomes significant, the heart muscle will be deprived of oxygen. Ischemia is a word used to describe a situation where there is not enough oxygen reaching the cells of the body. If the blood flow to the heart muscle is inadequate, cardiac ischemia can occur. Ischemia can cause chest pain. Chest pain due to ischemia is called angina. Blood flow to narrowed vessels can be improved by coronary artery bypass surgery or coronary angiography. MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION If the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen for a prolonged period of time, an area of the heart muscle can die. Dead muscle is called an area of "infarction". When an area of the heart muscle dies, it is called "Myocardial Infarction" or "MI". The most common cause for a myocardial infarction is blockage from a blood clot. Fatty disease of the blood vessels (called atherosclerosis) can promote clot formation. If a clot becomes large enough or breaks away from the wall of the vessel, it can block the flow of blood to an area of heart muscle.
One of the most serious types of myocardial infarction is called an "ST Segment Myocardial Infarction" or "STEMI". This type of heart attack is caused by the complete blockage of an important coronary artery. A large area of heart muscle can die with this type of heart attack. This can lead to serious and long term complications. This type of myocardial infarction is treated urgently by either introducing a special catheter and balloon into the blocked artery to "pop" it open, or by giving a clot busting drug like t-PA or Tenectaplase. A STEMI is diagnosed by specific changes on the electrocardiogram (ST elevation). When combined with other features such as chest pain and the elevation of special cardiac enzymes in the bloodstream, the diagnosis can be made quickly. This is important because prompt treatment may be able to reduce the amount of heart muscle damage. The Interventional Cardiac Catheterization department is located at University Hospital. If a patient has this specific type of heart attack and is a candidate for an urgent "balloon" procedure, a Code STEMI may be activated. The CCTC will transport the patient to University Hospital for the procedure. .
|
Image 1: Heart muscle with normal coronary arteries. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Last Reviewed: October 23, 2014