CAR-T cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy that is provided in a select number of cancer centres in Ontario. It is:
- Complex and requires specialized expertise
- Used to treat certain types of blood cancers
You and your doctor will decide together if this treatment is right for you.
What are white blood cells (WBCs)?
WBCs are an important part of the immune system and help the body fight infection.
What are T-cells?
T-cells are a type of WBC known as lymphocytes. They can target and destroy different cells, such as cancer cells, in the body.
What is CAR-T cell therapy?
CAR (Chimeric Antigen Receptor)-T cell therapy uses your body’s own immune system to target and fight cancer.
How CAR-T cell therapy works
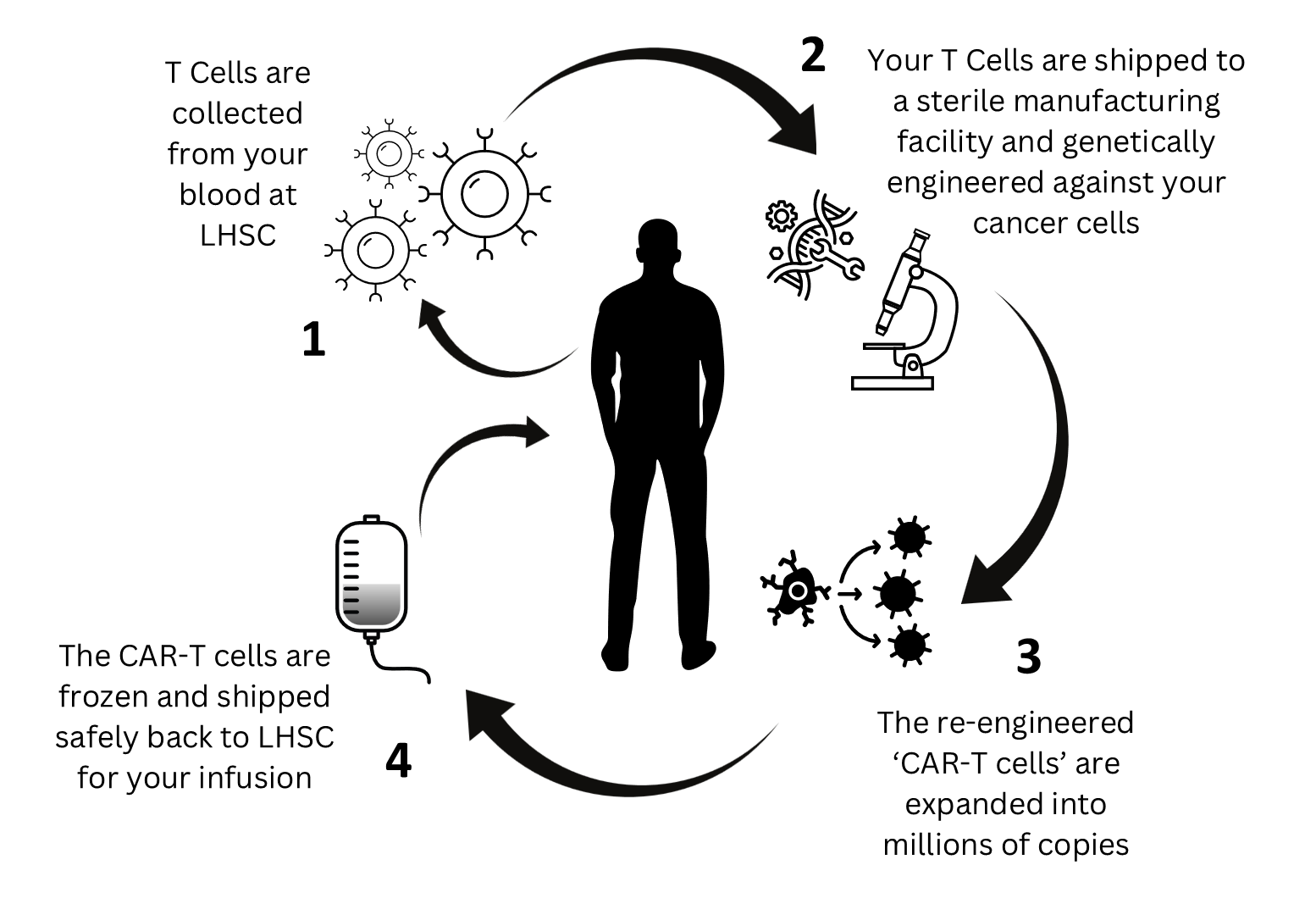
Image description
This circular, step‑by‑step diagram explains the CAR‑T cell process using icons, arrows, and a central silhouette of a person:
- T cells are drawn from a patient’s blood at LHSC. Illustrated with circulating cells and an arrow toward the central figure.
- The collected T cells are shipped to a sterile facility where they are genetically modified to recognize and target cancer cells. Represented with a DNA icon and a microscope.
- The newly engineered CAR‑T cells are multiplied into millions of copies. Shown with icons of modified cells.
- The CAR‑T cells are frozen, shipped back to LHSC, and prepared for infusion. Depicted with an IV bag and an arrow returning to the patient.
CAR-T cell therapy works by:
- Removing your own immune cells (T-cells) and changing them in a special manufacturing facility.
- In this process, a new receptor “CAR” is added onto your T-cells, which turns them into CAR T-cells.
- These CAR receptors attach to targets on the surface of cancer cells.
- The CAR T-cells are given through an intravenous (IV) infusion to target and destroy cancer cells.
When is CAR-T cell therapy used?
CAR-T cell therapy is used for adult patients with:
- Relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)
- Relapsed or refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
- Large B-cell lymphomas that are refractory to first-line chemoimmunotherapy or that relapse within 12 months of first-line chemoimmunotherapy
- Relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma following two or more lines of systemic therapy
- Relapsed cancer means your cancer has come back after responding to treatment.
- Refractory cancer means a specific treatment is no longer working to fight your cancer.
Will CAR-T cell therapy cure my cancer?
- It is not guaranteed that CAR-T cell therapy will cure your cancer, but it has brought positive results for many patients.
- Possible results of CAR-T cell therapy include complete remission, temporary remission, partial remission, or no response.
- Remission means the signs and symptoms of cancer have decreased or gone away.
- Your healthcare team will be closely monitoring your recovery and response to the CAR-T cell therapy.


